COVID-19 Severity in CLL Correlates With 3 Disease Characteristics
COVID-19 Severity in CLL Correlates With 3 Disease Characteristics
This article was originally published by Targeted Oncology
The severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) increases with age in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). However, age and the existence of comorbidities may not impact death from COVID-19, according to results from a retrospective international study published in Leukemia.
The study was conducted through a collaboration between the European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC) and CLL Campus. Study results came from a survey completed by 121 investigators at 118 sites around the world. Of the survey responder, 58 investigators confirmed that there were COVID-19 cases in their CLL cohort. The majority of the cases were identified in Europe (74%), followed by Asia (13.6%), Latin America (4.2%), Africa (3.4%), Canada (2.5%), and Australia (1.7%). Altogether, 156 cases of COVID-19 in patients with CLL were reported from a pool of 15,083 patients. COVID-19 cases were symptomatic and required hospitalization in 141 patients. Preventative measures for SARS-CoV-2 were reported by all but 0.8% of the sites.
“To the best of our knowledge, we present here the largest European series of patients with CLL infected by SARS-CoV-2 and experiencing COVID-19. Among the European cases (96.8% of the total) included in this project, almost 90% originated from Italy and Spain, hence mirroring the dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in Europe with Italy being the first country in a number of infected individuals followed by Spain, with a lower incidence,” wrote the study authors led by Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD of the Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele.
CLL Experts Favor Social Distancing, but Vary on Treatment Continuation Amid Pandemic
CLL Experts Favor Social Distancing, but Vary on Treatment Continuation Amid Pandemic
This article was originally published by AJMC
The survey is the latest attempt to figure out how best to manage patients with CLL amid the pandemic, given that patients with the cancer tend to be older in age, have comorbidities, and be immunosuppressed.
In a letter to the editor of the American Journal of Hematology, corresponding author Mazyar Shadman, MD, MPH, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, in Seattle, and colleagues reported on a survey sent to 62 CLL specialists in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Australia. Of those, 59 responded to at least 1 question, and 44 completed the entire survey.
When asked about social distancing recommendations for patients with CLL, 32% said they would advise patients to follow the same guidelines as the WHO and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend for the general public. Twenty-one percent said they would advise patients to follow those guidelines but also limit regular outings by asking friends to pick up groceries or medications for them. Another 35% went even further, saying patients with CLL should avoid work, even if they are essential workers. The remaining 12% said they would recommend all of the above, plus wearing N95 masks and gloves outside of the house.
In terms of testing, most experts said it was not necessary to test all patients with CLL for COVID-19. Specifically, 62% of experts said they would limit testing to patients who call to and report symptoms, and another 9.5% said tests should be limited to patients who come in for an office visit and report symptoms.
Still, while clinicians generally had a low bar for what types of symptoms warranted testing. “Most favored testing patients with any levels of reported symptoms, even with limited testing availability,” Shadman and colleagues wrote. “With unlimited access, 23% recommended universal testing.”
Though their approaches to social distancing and testing were in line with recommendations for the general public, the experts expressed caution when it came to continuation of outpatient therapy. Only 14% said CLL therapy should be continued unconditionally. Most (60.5%) favored treatment discontinuation, and 25.5% said they favored continuation only based on the specific clinical situation.
However, when it came to bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKis), such as ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and acalabrutinib (Calquence), the proportion of experts favoring unconditional treatment continuation was much higher, at 44%.
Shadman and colleagues said the more favorable responses concerning BTKi continuation may be due to concern about disease flares if treatment were stopped.
“Also, there is a theoretical benefit of BTKi’s in blunting the hyperinflammatory stage of COVID-19 disease by targeting macrophages and/or inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines,” they said.
Most experts (72%) recommended against the use of intravenous immune globulin (IVIG), though the authors noted that the survey was conducted in late March and early April, “before passive antibodies in the gammaglobulin pool would be expected.”
Shadman and colleagues said additional study is warranted to better understand the optimal approach to management of patients with CLL during the pandemic.
Age, Recent Treatment, Appear to Influence Severity of COVID-19 in Patients With CLL
Age, Recent Treatment Appear to Influence Severity of COVID-19 in Patients With CLL
This article was originally published by AJMC
Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who contract coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) face more severe symptoms if they are older, though recent treatment with antileukemic agents appears to have a beneficial, rather than detrimental, effect on outcomes, a new study found. The study also suggests that the presence of comorbidities does not lead to higher mortality rates.
The retrospective analysis is based on 190 patients with CLL who had confirmed COVID-19 cases between late March and late May. The results were published in the journal Leukemia.
Corresponding author Kostas Stamatopoulos, MD, PhD, of the Center for Research and Technology Hellas, in Greece, wrote along with colleagues that CLL is a “paradigmatic example” of a malignancy that has been associated with impaired immune responses to pathogens, which they said could have negative impacts on outcomes when patients with CLL contract COVID-19. The investigators added that antileukemic treatments could further hamper the immune system’s ability to fight off a virus like SARS-CoV-2, though they said it’s not a straightforward proposition.
“On the other hand, the severity of COVID-19 and [multiorgan failure] occurrence seem to be related to clinical and laboratory parameters of inflammatory response (lymphopenia, hypoalbuminemia, higher levels of alanine aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer) and markedly higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines (interleukin-2 receptor, IL6, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor-α),” they said. “On these grounds, therapies targeting inflammation (eg, IL6/IL6R antibodies or steroids) have been used and shown potential benefit in full-blown COVID-19 patients.”
In an effort to ascertain a real-world understanding of what patients with CLL who contract the virus should expect, Stamatopoulos and colleagues analyzed the 190 colleagues based on age, gender, and comorbidities; severity of COVID-19; and whether and how long ago they had been treated with antileukemic therapies.
The investigators found a strong majority (151, or 79%) of patients presented with severe symptoms, such as requiring oxygen or admission to an intensive care unit. Patients were more likely to have severe symptoms if they were aged 65 or older.
Recent treatment appeared to make a significant difference. Only 4 in 10 patients with severe symptoms had received antileukemic treatment within the past 12 months. However, among those with mild symptoms, 76.9% had undergone recent treatment. Among those with severe symptoms, the likelihood of hospitalization was lower if they had received therapy with ibrutinib (Imbruvica).
More than one-third (36.4%) of patients with severe symptoms died from COVID-19; versus just 1 of the 38 patients with mild symptoms succumbed.
Stamatopoulos and colleagues noted that the apparent link between age and mortality among patients with CLL tracks with known data from the general population. However, they said comorbidities did not appear to have a significant impact on whether a patient had mild or severe symptoms.
As for the impact of antileukemic therapies, the authors said a disproportionate percentage of their study population had been prescribed bruton kinase inhibitors. Thus, they did not have sufficient data to compare the impact of BTK inhibitors to other types of therapy.
Still, they said their data seems to support the idea that recent antileukemic therapy is beneficial against COVD-19.
“Altogether, these data seem to further underscore the possible protective role of specific targeted therapies against a dismal evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they said.
Changes in Management of CLL Due to COVID-19 Noted in Italy
Changes in Management of CLL Due to COVID-19 Noted in Italy
This article was originally published by Cancer Therapy Advisor.
The clinical management of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) was altered across Italy in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey study published in Blood.
“What is starting to emerge is an impact on the routine work-up of patients, on treatment choices, and the enrollment and adherence to clinical trials,” the authors wrote.
The authors sent a survey to 33 hematology centers across Italy in early April that included questions about testing strategies for COVID-19; the effect of the pandemic on diagnosis, management, and the outcomes of patients with CLL; and the adherence to clinical protocols. The survey data was based on 9930 patients with CLL, which represents approximately one-third of all patients with CLL in Italy.
Although the minimum testing requirements mandated by law were followed by all centers, only 30% of centers tested asymptomatic patients without any known contact with a COVID-19 case prior to initiating CLL treatment. The authors said that this “reflects the higher capacity of some regional health systems to performed analyze nasopharyngeal swabs.”
CONTINUE READING
Of the 9330 patients with CLL, 47 (0.5%) patients were symptomatic and tested positive for COVID-19.
Most centers reported a decrease in the number of newly diagnosed CLL cases, likely due to a decrease in the use of peripheral laboratories for diagnostic work-up, the authors said. In addition, 15.2% of centers reported that delays and difficulties in an accurate diagnostic work-up has occurred due to a reduction in personnel.
New treatment initiation was delayed in 79% of centers, and 24% of centers reported a delay in ongoing therapy. Delayed post-treatment restaging also occurred in 30.3% of centers.
The sample size was not large enough to characterize patient outcomes due to COVID-19 or the effect of anti-CLL treatments. However, there was a mix of patients who were receiving active first-line or salvage treatment vs no active treatment.
The mortality rate in this cohort was 30.4%. “The mortality rate for symptomatic COVID-19 patients amongst the general population was 13.4% and 25.5% in the 70- to 79-year-old population,” the authors noted.
Clinical trial enrollment and follow-up of patients on a clinical trial protocol was reduced in two-thirds of the centers.
The authors concluded that this survey has revealed that COVID-19 “has started to impact on the number of new cases, on the adequate follow-up of treated patients, on the number of patients enrolled in clinical trials, and on the monitoring of such patients.”
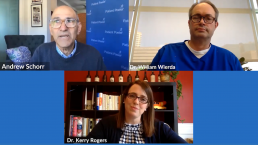
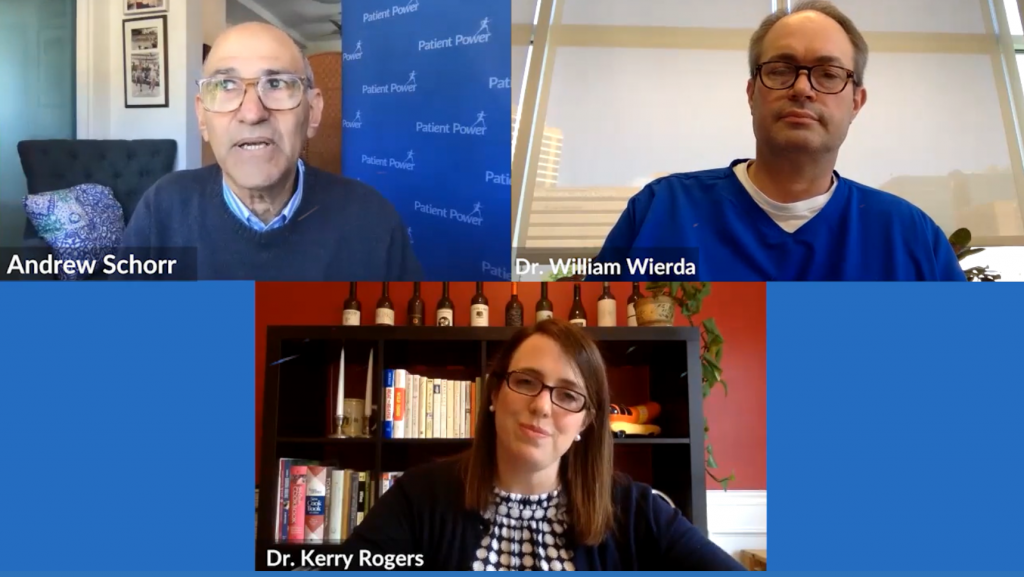
Coronavirus: Separating Fact From Fiction for CLL Patients
Coronavirus: Separating Fact From Fiction for CLL Patients
“We’re learning every day, and we’re modifying and adjusting based on what we learn,” says Dr. William Wierda, from The University of Houston MD Anderson Cancer Center, as new information continues to come to light on the novel coronavirus.
Can cancer medicines be used to treat COVID-19? Does the effect of the virus vary by CLL subtype? Is ibrutinib (Imbruvica) being mixed with Coca-Cola? Watch to hear expert perspectives on questions like these and more.
With much misinformation circulating online, Dr. Wierda and Dr. Kerry Rogers, from The James Comprehensive Cancer Center at OSU, joined Patient Power to help chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients separate fact from fiction and explain how care is being modified during the pandemic.
This program is sponsored by Pharmacyclics and Janssen. These organizations have no editorial control, and Patient Power is solely responsible for program content.
Click the image to view this video.
Originally published on Patient Power
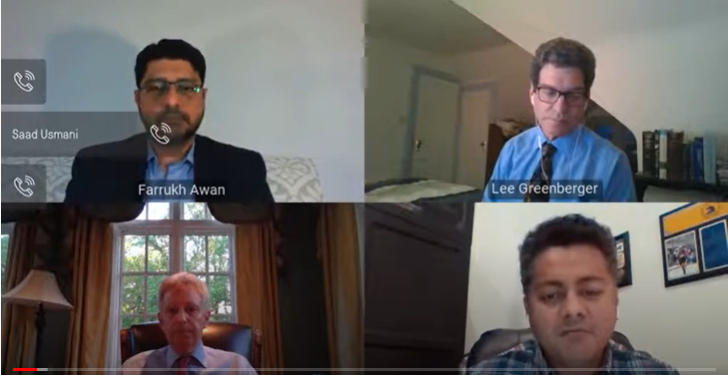
COVID-19's Impact on How Patients with CLL, Myeloma Have Received Treatment
COVID-19's Impact on How Patients with CLL, Myeloma Have Received Treatment
CURE® recently invited patients, survivors, caregivers, advocates and health care professionals to attend its first-ever live webinar, “Hear from the Experts: COVID-19 & Cancer Care for Patients.”
Sponsored by Janssen and Pharmacyclics, the webinar was designed to provide those affected by chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and myeloma with information and updates as it pertained to the current landscape of cancer care during the uncertain times of the new coronavirus (COVID-19).
Dr. Saad Usmani, chief of the Plasma Disorders Program and director of clinical research in hematologic malignancies at the Levine Cancer Institute served as the moderator for the webinar. Panelists included:
- Dr. Zainab Shahid, medical director of bone marrow transplant infectious diseases at the Levine Cancer Institute
- Dr. Farukh Awan, director of the Lymphoid Malignancies Program at the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center at UT-Southwest
- Dr. Ian Flinn, director of the Lymphoma Research Program at Sarah Cannon Research Institute
- Dr. Lee Greenberger, chief scientific officer at the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society
In the first part of this series, Dr. Farukh Awan addresses how the pandemic has affected his practice, as well as how it has impacted how patients with CLL and myeloma have received care.
Awan: We’re all learning. This is something that none of us have experienced before, so we’re learning more and more about the virus with every passing day. There’s more data coming out. There’s a lot of new clinical trials happening, so everything is happening at the same time we are all trying to do the best we can to decrease the spread of this so we can better manage our patients who do get infected and that would not overwhelm the system.
In line with that, every institution has instituted a policy that suits their needs. Fortunately, in Dallas we started with social distancing early and I think we were able to keep the numbers fairly manageable. And yet, we still had to make a lot of changes to the way we practice.
In terms of outpatient management, we have limited the number of visitors that come in with the patient. We try to keep them outside of the clinic area. We also have tried to make the most of our electronic visits so that the least number of patients get exposed to the staff, and vice versa. We have also started utilizing local labs, which are a lot of times not as busy as the oncology clinics and cancer centers. Those labs then give us the results from the blood work that we need. I think we’ve utilized all of these approaches on the outpatient side. We’ve also been fortunate that we have a service for drive-through testing for patients who have active symptoms. We are trying to get them through the drive-through testing and if they are positive, then they’re asked to quarantine at home.
For those who do get really sick and need to go to the hospital, the ER has a system where everybody gets quarantined on arrival. They get tested in a timely manner with a rapid test for their COVID-19 and if they are positive, they are then sent to a specific isolation floor meant for those patients. There are mechanisms in place, both on the outpatient and inpatient side, which have tried to minimize exposure to patients, family members, and staff at the same time.
As far as for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who are concerned, a lot of our patients can afford to wait a little bit to start their new treatment. For patients who are not actively getting treated, we do plan on delaying their treatment until at least we have some idea of better treatment modalities and if their symptoms can be managed by other approaches. For those who are on active treatment, we are trying to continue those treatments while trying to minimize their return visits and we’re trying to do that electronically as much as possible, either via telephone calls or through a video visit. Either option is being utilized so that patients can limit their back and forth to the clinic.
We know that our patients with CLL are especially at a high risk of getting infections. Infection-related complications are one of the leading problems in our patients. We expect that our patients would be at an extremely higher risk and that’s why we are also advising that they socially distance themselves from any known patient or persons who might have the virus. We are now also learning that there is a fairly large group of patients, or people in the community, who would have asymptomatic disease and they can potentially spread the disease to a lot of other people without even knowing that they have the virus, and I think that’s very scary for our patients since they are immunocompromised at baseline, even without treatment.
It’s a unique challenge. We are recommending that all our patients with CLL practice social distancing, minimize exposure, and even if they don’t have to go out for groceries they shouldn’t. I think if we can do that over the next few months, hopefully, we can right this and hopefully we will get our patients through it without having any serious complications.
On the other hand, some patients with lymphoma can wait to start treatment, some of them cannot. In some aggressive lymphomas, the treatments need to be started right away. For those patients who need to start treatment right away we are following them very closely for any symptoms. If they exhibit any symptoms, like fevers or a cough or any upper or lower respiratory tract symptoms, we are testing them before we give them any chemotherapy. If somebody is positive for the virus, we are not using chemotherapy for those patients and we are trying to delay chemotherapy as much as possible.
For patients already on treatment and need to be admitted to the hospital we are screening them with a test 48 to 72 hours prior to their admission to the hospital, and once they’re negative, they can then start their treatments. We’re trying to use all these resources that are available to us to try to minimize the risk, again, to the staff and to patients and to prevent any complications that might happen in the future.
Finally, I’d like to make a point regarding stem cell transplants and CAR T. These can be potentially curative options for our patients. We also realize that a lot of our patients will get extremely sick during that process. So, we have multiple challenges with regards specifically to stem cell transplants and CAR T. We’ve also learned that the Red Cross and blood banks are being stretched and that their resources are limited. The number of donors is limited. Since there aren’t a lot of donors like we normally would have, getting access to blood products can be a challenge for our transplant patients, especially if they need blood transfusions and platelets.
We’re trying to very specifically look at all the factors for every patient who is undergoing an autologous transplant, or a CAR T cell treatment and we are trying to select the patient who absolutely needs to proceed with it. We are taking that patient to transplant and are employing a multitude of tests at various time points and making sure there are no visitors during their hospital stay, and as much as possible we are ideally using electronic visits for follow-up to minimize exposure.
Have we done transplants in the last few months? Absolutely. We’ve also done CAR Ts and we have successfully and safely gotten patients through it, but it’s challenging. It can be done but we have to be extremely careful that we minimize exposure to our patients and hopefully we can all get through this.
Originally published on Cure
How COVID-19 Has Impacted Clinical Trials for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
How COVID-19 Has Impacted Clinical Trials for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Many patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) rely on the outcomes of clinical trials that examine new ways to treat the disease. But with the new coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic changing the way health care is provided around the country, so too is participation in these trials, according to Dr. Brian Koffman, the co-founder, executive vice president and chief medical officer of the CLL Society.
CURE® recently spoke with Koffman about how clinical trial participation has become more flexible over the course of the pandemic in an effort to keep immunocompromised individuals like those with CLL safe, by utilizing things like telemedicine and localized care to avoid exposure to the virus.
Originally published on Cure
CLLANZ calls for home-based treatment for CLL patients during COVID pandemic
CLLANZ calls for home-based treatment for CLL patients during COVID pandemic
Last week CLL Advocates New Zealand wrote to Pharmac requesting them to provide temporary access to ibrutininb (taken in tablet form at home) for del17p and RR patients, and for newly diagnosed fit and unfit patients.
Read the letter below or download the letter here.
—
Dear Peter Murray, Deputy Medical Director
Thanks for your email clarifying the nature of changes Pharmac has made under Special Authority with respect to the management of cancer medicines, in light of the current COVID-19 crisis.
You have asked if I have any ideas on this issue that I would like to put forward for consideration and indeed I do. They concern risks posed by aspects of the current treatment of patients with CLL, as follows.
- A fellow Trustee of CLL Advocates NZ (CLLANZ), haematologist Gillian Corbett, has raised serious concern about the risks posed to patients in the administration of the current funded standard-of-care treatment for patients with del17p and relapsed refractory CLL. She has a patient starting treatment this week who had to go across town for urgent lab testing twice in one day, and again the following morning for tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) management. She noted that IV hydration needs to be considered in these patients, and that her patient will likely need to have more urgent blood tests during the coming week. She will need to have the procedure repeated next week. Gillian is very concerned about patients like this one having to put themselves at risk by going to the labs where there is likely to be a long wait, which in their immune-suppressed state would increase their risk of infection, including COVID-19.
For this reason we would like to propose that a change to CLL treatment be made under Special Authority to enable ibrutinib, which is taken in tablet form at home, to be funded temporarily for del17p and relapsed refractory CLL patients. In addition to being a home-based treatment, ibrutininb requires very little monitoring, infrequent blood tests and infrequent attendance at hospital (outpatients).
- We also propose that the Special Authority enables newly diagnosed fit and unfit patients to access ibrutinib, to avoid the need for chemotherapy or a delay in initial treatment. Again this would be a temporary SA to be in place until such time as patients can safely undergo in-hospital care.
- Finally we propose that the Special Authority for ibrutininb should also apply to treatment for CLL patients who are having intravenous therapy in a hospital setting, such as rituximab or obinutuzumab, which is given by infusion and requires, particularly initially, prolonged attendance at the chemotherapy department which is highly undesirable at this time of the COVID-19 epidemic.
As you would know, patients with CLL are immuno-compromised, and most are in the most at-risk age group, so we believe for all these reasons Pharmac should move quickly to make these changes.
I don’t have an accurate understanding of the numbers of patients this would involve, and I’m currently canvasing CLLANZ subscribers for further input on this issue. But I understand there has been a significant drop in people presenting with CLL, no doubt due to the general pattern of people avoiding going to the doctor. The same may be true of RR patients. I understand that HSANZ may be looking at the likely number of patients who would benefit from these changes, but that the numbers involved are likely to be very small and the costs therefore low.
It seems to me, at a time when so much effort is going in to saving lives, implementing this proposal would be a most worthwhile contribution from Pharmac.
I’d be very happy to discuss this with you or provide any further information you may require, and look forward to hearing back from you on this request.
Kind regards
Neil Graham FRACP, FRCP
Executive Director
CLL Advocates NZ
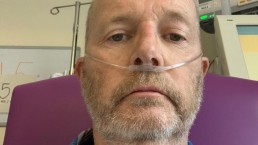
How it feels to be in intensive care with COVID-19 - a survivor with CLL
Coronavirus: This is how it feels to be in intensive care with COVID-19 - a survivor's graphic story
Robin Bowler, a lottery and gaming consultant, feared he’d never see his kids again after contracting coronavirus and ending up in intensive care – but a voice in his head somehow got him through.
This is a story of hope, his story – a survivor’s story:
If you were to write down the classic set of conditions that a single person may have, in which COVID-19 could thrive, you would probably end up with a profile that looked remarkably like me.
I am 58, I have asthma, I have one of those much-mentioned “underlying health conditions” – namely chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) – I am blood group A (reportedly more susceptible to the more aggressive form of coronavirus, with a high proportional death rate), and until recently, drank more than I should.
On the plus side, I happen to have a good level of underlying fitness and spend a lot of time outdoors.
So that’s me. Well, almost.
I returned from Italy on 7 March and first began to feel some slight chestiness during the evening of Monday 9th. Following a call with 111 I was recommended for a COVID-19 test, which was done on the 13th and I received confirmation from Public Health England by telephone the following Tuesday 17 March.
In the meantime my previously mild condition had turned for the worse into flu-like symptoms, and I could feel an infection growing in my chest.
By the Thursday night I was having serious problems breathing. So at 5am on Friday 20 March I called 111 again and was hospitalised that morning in an isolation room in the Lulworth ward of Dorset County Hospital.
Incredibly, at this time I did not feel particularly frightened, although the enormity of my decision to go to Italy was dawning on me – as was the realisation that if this got really serious, I was on my own.
There would be no family to visit, no contact with NHS staff other than that which was essential, an intercom to speak to front-line staff safely. Just me and the four walls of my room and its contents.
By Sunday 22 March it was clear that the committed care I was receiving from the doctors and nursing staff on Lulworth ward was simply not working.
A second chest X-ray revealed that what had been originally described to me as a “pneumonia” had worsened, my temperature spikes were climbing dangerously close to the 40C mark on multiple occasions, and I was weakening by the hour.
At this time, what was really bothering me was the fact that there had been a suggestion that they would send me home within a day, and I knew that I would not cope without the specialist care available within the hospital.
My concern levels rose to full anxiety and therefore late that afternoon I asked to speak with a doctor and, during a dialogue in which I became very emotional, he calmly reassured me that there was no way I would be sent home against my wishes, and that they would not consider discharge unless they were sure I was safe.
Shortly afterwards, I was visited by a senior consultant who I believe introduced himself as head of critical care at DCH.
He informed me that, having reviewed my situation, the decision had been taken to move me to intensive care as a precautionary measure, warning me in no uncertain terms that this was going to be a long haul.
He then fixed me with a hard look and added: “You may not survive this.”
I responded (equally calmly, I think): “I’ll do what I have to do.”
But inside, I could feel my confidence crumbling, my fear rising to hitherto unknown levels, and my mind starting to run amok with self-recrimination, longing to be with my (adult) children Natasha (Tash) and Luke, and a new sense that I had moved from a virus into a life-threatening situation which my combination of “underlying health conditions” just may not be able to cope with.
Within less than half an hour I was in intensive care, isolated in a room that looked like it was normally the area where staff monitored patients from. I had never felt so alone in all my life.
By midnight, I was busily convincing myself that I could well be dying and it was all my own fault. The thought of never seeing Tash or Luke again was simply unbearable, but in my mind and in fact, this was a realistic scenario that now existed.
I was being monitored by a team led by a senior consultant anaesthetist, who was asking me if I thought I could continue with the oxygen supply through my nose as a preferable alternative to full anaesthesia, intubation and being placed on a ventilator for an indefinite period of time.
Going onto a ventilator meant replacing my lungs with a mechanical breathing apparatus while disabling all my normal involuntary muscular activity involved with breathing.
After an hour I realised two things: firstly that my mental capacity to make what amounted to life and death decisions was by now seriously impaired and that I was incapable of making good decisions; and secondly that I was haunted by the fact that the second X-ray had been worse than the first, and so I was convinced that the current oxygen treatment was similarly not up to the job.
By 2am the decision was taken to “put me to sleep” and in a strange way I welcomed the ability to surrender all decision-making to these cool-headed, professional experts who knew much better than I did the risks I faced and trade-offs that were involved.
The process of being “put to sleep” was terrifying.
I was surrounded by medical staff, each with their own responsibility in the process, and all calmly and clearly directed by the senior consultant anaesthetist, who was pressing a face mask down on to my face with a force that made me feel that I could no longer breathe, while verbally reassuring me I was safe and would be taken very good care of.
I thought at the time that this could be the last I see of this life, and at the suggestion of the anaesthetist, thought of Tash and Luke for all I was worth, after which I remember nothing more of that night.
As it turned out, I was on the ventilator for approximately 36 hours during which time I remember nothing, but during which time I was kept alive by the skill of the medical teams and their sophisticated machinery.
I was brought out of the anaesthetic late afternoon on Tuesday 24 March and extubated (taken off the ventilator), and I can remember waking up, seeing blue sky through a window, and thinking “I’m still alive”. I was in the high-dependency unit by this time, and just the presence of natural daylight had the most profoundly positive effect upon me.
My immediate thought was to get a message to Tash and Luke that I was conscious again and I made that request (almost certainly in much more garbled form than I credited myself with at the time) which was duly granted.
The other feeling I had immediately was that I felt less exhausted than I had been that Sunday night, and much more ready for the prolonged fight ahead.
I was on oxygen support for the rest of Tuesday 24th, overnight and into Wednesday 25 March.
By this time I was coughing up thick globules of blood and sputum which had accumulated in my bronchus as a result of the intubation.
This was a serious problem, because every time I coughed this horrible stuff up, it made me vomit as well, which was thoroughly interruptive of the oxygen supply which was so essential to my survival at this point; and for the medical staff because it exposed them to more pure COVID-19 infectious material.
To give an idea of how sick I was at this time, one indicator called CRP (C-reactive Protein) showed that my reading was 340, where a non-infected person’s score should be minus 2.
My temperature was continuing to spike around the 40C mark (the point at which multiple organ failure can begin to set in), my blood saturation levels were poor, my blood pressure was “through the roof” (quote, unquote), and just about every other data point was out of whack.
Despite 36 hours on the ventilator, the virus was rampant within my body, particularly my lungs, and it was highly questionable whether I would make it through or not, with all my in-built disadvantages.
During the afternoon of Wednesday 25 March the team of consultants and doctors who were making collaborative decisions every hour made the decision to place me on CPAP support (continuous positive airway pressure) for however long may be necessary.
This involved a very tight-fitting face mask, through which a constant stream of pure oxygen is pumped directly into the lungs – in my case starting at 55 litres per hour.
I had two main concerns at this point: first, to keep breathing, and second, to try to suppress the coughing up of blood and sputum as I had no way of expelling it – the doctors told me I had to swallow it.
This was appalling to me, so we hit upon a compromise where I could use a thin suction tube to slide inside the CPAP mask without interrupting the flow of oxygen. This was more difficult and less practical than it sounds, and I soon found myself forcing myself to swallow the foul stuff, as I had been directed to. I was reminded of my defiant response “I’ll do what I have to do”.
Once the CPAP was started, I was on all sorts of medication. I had multiple cannulas in both arms, one in an artery, and one in my neck which allowed fluids to be poured down the back of my throat into my stomach – the water was okay, but the potassium was horrible.
But one of the medications was to reduce my level of anxiety, and so for the next 48 hours I became quite hallucinogenic as my mind was eased away from the drama of my situation, and so it started to float freely and at times bizarrely in all manner of directions.
During this 48-hour period, I found myself conversing with unknown others in a range of different accents from around the United Kingdom. Broad Scots, Northern Irish, Welsh, Geordie, Scouse, Cockney, Cornish – it was like taking a virtual tour of the UK and chatting with very amenable strangers who were full of good advice and encouragement.
And at times I would slowly descend into a sunny glade where people were relaxing, and as I got close enough to them to begin to discern their features, they vanished as quickly as they had appeared.
Other times I was floating in a circular motion inside a large natural bowl of thick green vegetation, but try as I might, I could never see the rim of the bowl and the sky above.
And all this time, the constant refrain of WHOOSH, HISS, WHOOSH, HISS, WHOOSH, HISS, dominating the weird version of consciousness that I found myself in. And a clear voice in my head then reminded me that I was fighting for my life.
It said that I was in the Staying Alive Factory, and that if I wanted to survive, I needed to stay on this noisy, uncomfortable, frightening production line; and that alternatively, if I fell off the production line, I would not make it through. So that was it.
Then the voice reminded me that I had a lot of explaining to do to Tash and Luke, and so I resolved there and then to remain on the production line – “I’ll do what I have to do”.
After approximately 48 hours on the CPAP, the same head of critical care came and asked how my breathing was.
The anti-anxiety medication must have been reduced or stopped by this time, because I clearly remember the conversation.
“Mmmch bttr,” came my reply.
“Sorry, did you say your breathing feels better?” repeated the doctor.
“Much better,” I forced out through the oxygen flow, the tight-fitting CPAP mask, and my by now completely dry mouth, throat and tongue.
I also felt instinctively that the industrial strength antibiotics they had been pumping through my body for days had finally got on top of the vicious bacterial infection in my lungs.
I had stayed on the production line, and I suddenly knew I could get past this. I could breathe to a depth that felt like it was self-sustaining (not actually quite the case at the time), and during the last few hours on the CPAP, I began to communicate by writing short notes on a clipboard given to me by one of the doctors.
One of the first notes I wrote was the question: when can I eat and drink something?
Within what seemed like a couple of hours, the CPAP was removed and replaced with a much gentler oxygen supply through my nose.
The instant calm that descended with the removal of the WHOOSH, HISS tyranny made me think I had moved from the main production line of the Staying Alive Factory to the body shop where, instead of destroying bad things and building back up good things, the focus moved to refined monitoring of what my body was able to do for itself again.
It was a beautiful day outside, that I could see from my bed. And it was a beautiful day inside my head, as I contemplated that I maybe would be seeing Tash and Luke again, and that my time had not yet come.
The rest, as they say, is history.
I was moved to Moreton ward, a convalescence ward where I was weaned off the oxygen supplies, given regular meals, and the recovery physio began. I was declared medically fit for discharge on Wednesday 1 April (an auspicious day if ever there was one), and I was reminded what a fool I’d been to play fast and loose with my health just to go on a skiing holiday. A mistake I will never make again.
Of course, there is no such thing as the Staying Alive Factory, which was an invention of my befuddled mind at a time of extreme health crisis.
What there is is the dedicated expertise, courage and commitment of the consultants, doctors, nurses, physios, Ancillary staff, and undoubtedly many, many others, of the NHS who collectively saved my life.
It may feel like a factory when you are undergoing such intensive care, but the key word here is care. It is to that care that I owe my life, and I will be forever grateful.
Originally published on Sky News
Patient With CLL May Have Had Longer COVID-19 Incubation Period
Patient With CLL May Have Had Longer COVID-19 Incubation Period
A case report out of China suggested that clinical and biochemical data of COVID-19 might have been partly masked in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Specifically, a patient presenting in Wenzhou, China, with CLL who was diagnosed with COVID-19 appeared to have a disease incubation period of about 25 days. The patient had traveled to Wuhan between January 12-18, 2020, before traveling back to Wenzhou and self-isolating for 14 days. He presented to the hospital on February 16 after four days of symptoms.
“Without the complete travel history, COVID-19 infection was not initially suspected, because his whole blood cell and lymphocyte counts were high because of his chronic lymphocytic leukemia masking a potential infection,” the case report authors wrote. “However, the attending physician noticed that although symptoms could be the result of a recurrent infection, his chest CT scan resembled that of a patient with COVID-19.”
After testing positive, the patient began treatment with reduced dose of oral chlorambucil to treat his condition due to CLL and received the recommended treatment for COVID-19 in China: nebulized α-interferon (5 million IUs) twice per day, intravenous human immunoglobulin (20 g) once per day, and intravenous methylprednisolone (40 mg) every 12 hours.
The patient had relapsing fever PaO2/FiO2 less than 300 mm Hg and a sequential organ failure assessment score of 4. Noninvasive ventilation therapy was given until dyspnea subsided on day 8 of treatment. Treatment was changed to low-dose methylprednisone every 12 hours with oral chlorambucil twice per day for the next 4 days.
Follow-up CT showed substantial improvement and the patient’s temperature also returned to normal. A repeat COVID-19 test showed the patient remained positive for the virus and an additional 7 days of observation was recommended.
Based on this case, the authors said better diagnostic strategies could be used for diagnosis, and individuals with compromised immune status may be subject to a longer disease incubation period.
“It remains uncertain whether the combination of chemotherapy, corticosteroids, α-interferon, and immunoglobulins could work synergistically in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and COVID-19,” they wrote.